Getting started with Meteor SDK
A quick guide to get you started with the meteor runtime connector SDK.
After reading this guide, you will be able to connect with the meteor browser extension, create, load, update and monetize a file.
Before we start, please make sure you have created your meteor-app and defined the data models you want to use in your app using the create-meteor-app framework.
Prerequisites
Install JS SDK
pnpm install @meteor-web3/connectorStep 1: Initialize the connector
// After installation, you can import the SDK and initialize the meteor connector.
/** Import Meteor Connector SDK */
import {
Connector,
MeteorWalletProvider,
MeteorWebProvider,
} from '@meteor-web3/connector';
/** Or initialize the meteor connector class object with MeteorWebProvider*/
const connector = new Connector(new MeteorWebProvider());Step 2: Connect with user wallet
import React, { useState } from 'react';
/** Import Meteor Connector SDK and types */
import {
Connector,
WALLET,
MeteorWebProvider
} from "@meteor-web3/connector";
/**
* Initialize the Meteor Connector
*/
const connector: Connector = new Connector(new MeteorWebProvider());
const App: React.FC = () => {
const [wallet, setWallet] = useState<WALLET>();
const connectWallet = async () => {
try {
const res = await connector.connectWallet({
provider: window.ethereum
});
setWallet(res.wallet);
return(res.address);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
};
return (
<button onClick={connectWallet}>
Connect Wallet
</button>
);
};
export default App;The connectWallet function receives an optional parameter wallet to specify which wallet to use.
enum WALLET {
METAMASK = "MetaMask",
WALLETCONNECT = "WalletConnect",
COINBASE = "Coinbase",
PARTICLE = "Particle"
}Step 3: Create capability
import { RESOURCE } from '@meteor-web3/connector';
const app = 'YOUR_APP_NAME';
const createCapability = async () => {
const pkh = await connector.runOS({
method: SYSTEM_CALL.createCapability,
params: {
appId,
resource: RESOURCE.CERAMIC,
wallet,
},
});
return pkh;
};This will open a popup window to ask for user permission to connect with the application. We use Sign-in-with-Ethereum signatures to authenticate the user approvement. The popup shall be like this:
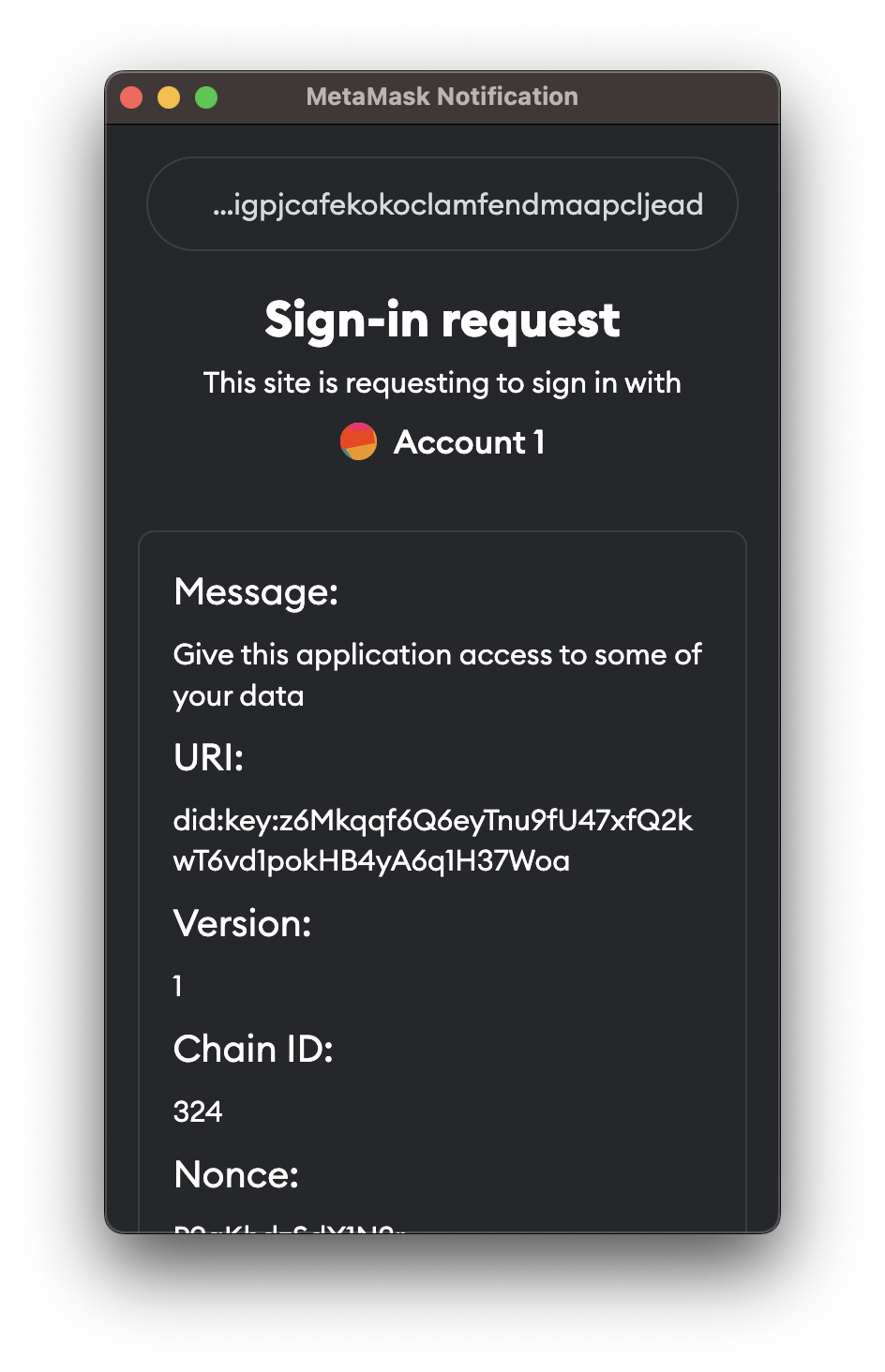
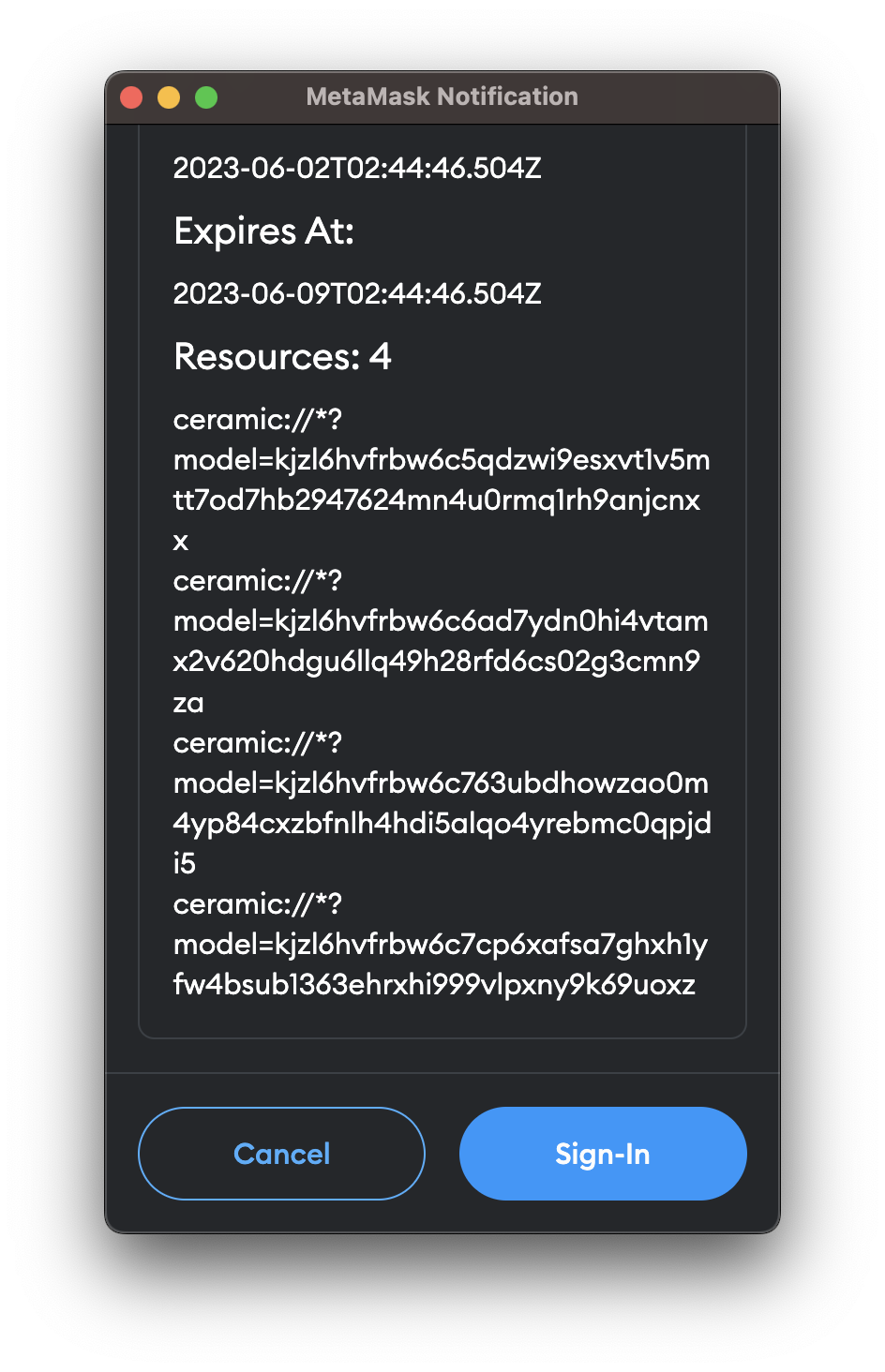
It returns: pkh: string - a pkh 'DID' you may use to interact with the data resources later.
Step 4: Create a file
File is the smallest unit of data in our system.
Unlike IPFS CID which 1. cannot be changed after upload 2. are discrete and not related, files can be updated after creation and linked between each other.
Each file belongs to a data model. For example, if you have created a data model called post as a data structure for posts in a social app
type post @createModel(accountRelation: LIST, description: "post") {
author: DID! @documentAccount # DID of the user who created this post
version: CommitID! @documentVersion
appVersion: String! @string(maxLength: 100)
text: String @string(maxLength: 300000000) # text content of the post
images: [String] @list(maxLength: 10000000) @string(maxLength: 2000000) # images of the post
videos: [String] @list(maxLength: 10000000) @string(maxLength: 2000000) # videos of the post
options: String @string(maxLength: 300000000)
createdAt: DateTime! # time when the post is created
updatedAt: DateTime! # time when the post is updated
}createIndexFile under this post model is how you create posts.
const encrypted = JSON.stringify({
text: false,
images: false,
videos: false,
});
const res = await connector.runOS({
method: SYSTEM_CALL.createIndexFile,
params: {
modelId,
fileName: "post1",
fileContent: {
modelVersion: "0.0.1",
text: "hello",
images: [
"https://bafkreib76wz6wewtkfmp5rhm3ep6tf4xjixvzzyh64nbyge5yhjno24yl4.ipfs.w3s.link",
],
videos: [],
createdAt: new Date().toISOString();,
updatedAt: new Date().toISOString();,
encrypted,
},
},
});return example
{
"pkh": "did:pkh:eip155:1:0xb4D93398f6F3FB5EE4436D1aE93b32d65693a799",
"appId": "a3f0ac63-ff7d-4085-aade-c04888b71088",
"modelId": "kjzl6hvfrbw6catek36h3pep09k9gymfnla9k6ojlgrmwjogvjqg8q3zpybl1yu",
"fileContent": {
"content": {
"text": "hello",
"images": [
"https://bafkreib76wz6wewtkfmp5rhm3ep6tf4xjixvzzyh64nbyge5yhjno24yl4.ipfs.w3s.link"
],
"videos": [],
"createdAt": "2023-11-02T08:04:53.380Z",
"encrypted": "{\"text\":false,\"images\":false,\"videos\":false}",
"updatedAt": "2023-11-02T08:04:53.380Z",
"modelVersion": "0.0.1"
},
"file": {
"fsVersion": "0.11",
"contentId": "kjzl6kcym7w8y8wx1zuujmssq4wj6o6paynupzmidz7izcsiqwgpnt1uyo9lg2a",
"contentType": {
"resource": "CERAMIC",
"resourceId": "kjzl6hvfrbw6catek36h3pep09k9gymfnla9k6ojlgrmwjogvjqg8q3zpybl1yu"
},
"fileName": "create a file",
"fileType": 0,
"createdAt": "2023-11-02T08:04:56.699Z",
"updatedAt": "2023-11-02T08:04:56.699Z",
"fileId": "kjzl6kcym7w8ya3kyamskljmo181t6z3vz6px0w90c76ea3m28g994t58341ijt"
}
}
}To create a file under a specific model, you need to specify the model id and
ensure your app has the capability to write data under this model. if not,
please use createCapability to create a capability for the model first.
Step 5: Load a file
You can load an indexFile's content by its id.
await connector.runOS({
method: SYSTEM_CALL.loadFile,
params: indexFileId,
});You can also load multiple indexFiles under a model using loadFilesBy.
await connector.runOS({
method: SYSTEM_CALL.loadFilesBy,
params: {
modelId,
pkh,
},
});The pkh field is optional. If not specified, it will return all streams under the model. Otherwise, it will return streams under the model that are created by the user.
Step 6: Update a file
const date = new Date().toISOString();
const encrypted = JSON.stringify({
text: true,
images: true,
videos: false,
});
const res = await connector.runOS({
method: SYSTEM_CALL.updateIndexFile,
params: {
fileId,
fileName: 'new-post1',
fileContent: {
appVersion: '0.1.0',
text: 'hello',
images: [
'https://bafkreib76wz6wewtkfmp5rhm3ep6tf4xjixvzzyh64nbyge5yhjno24yl4.ipfs.w3s.link',
],
videos: [],
createdAt: date,
updatedAt: date,
encrypted,
},
},
});updateIndexFile shares the same parameters as createIndexFile, except the fileId is required.
and the return value is in the same format as createIndexFile.
Step 7: Monetize a file
The native method is as follows.
import { Currency } from "@meteor-web3/connector";
const res = await connector.runOS({
method: SYSTEM_CALL.monetizeFile,
params: {
fileId,
monetizationProvider: { ... },
encryptionProvider: { ... }
},
});It is recommended to use monetizeFile method under the DataToken (opens in a new tab) class from assets-sdk (opens in a new tab) directly.
import {
DataToken,
DEPLOYED_ADDRESSES,
} from '@pyra-marketplace/assets-sdk/data-token';
const dataToken = new DataToken({
chainId,
fileId,
connector,
});
const res = await dataToken.monetizeFile({
actionsConfig: {
collectAction: {
currency: DEPLOYED_ADDRESSES[chainId].WMATIC,
amount: 1000,
},
},
});Step 8: Purchase a file
import { DataAssetParser } from '@pyra-marketplace/assets-sdk/data-asset';
import { DataToken } from '@pyra-marketplace/assets-sdk/data-token';
const dataAssetParser = new DataAssetParser(connector);
const dataAsset = await dataAssetParser.parse(indexFileId);
const dataToken = new DataToken({
chainId: dataAsset.chainId,
fileId: dataAsset.fileOrFolderId,
assetId: dataAsset.assetId,
connector,
});
const collectionId = await dataToken.collect();This will send a transaction to mint an NFT to the user's wallet address. The NFT is the access credential to the data.
monetizeFile and collect functions are on Mumbai testnet for now.
After purchase completed, you can load the file content using unlockFile function.
await connector.runOS({
method: SYSTEM_CALL.unlockFile,
params: indexFileId,
});s